atDNA is short for Autosomal DNA. Autosomal DNA is a term used in genetic genealogy to describe DNA which is inherited from the autosomal chromosomes. An autosome is any of the numbered chromosomes, as opposed to the sex chromosomes. Humans have 22 pairs of autosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes (the X chromosome and the Y chromosome).
Autosomal DNA Testing
Autosomal DNA tests have been designed to look at chromosomes 1 - 22 to trace all of your ancestral lines for five generations or more. This test is offered by AncestryDNA, FamilyTreeDNA, and 23andMe. They confidently identify relationships within 5 to 6 generations by analyzing thousands of data points on your 1 Autosomal chromosomes. Your results are automatically compared to others that have tested with the company that you chose. You are then given a list of matches and the predicted relationship to you.
The number and size of shared segments are used to determine how recently any two people are related. The only challenge that you will come across is finding which particular branch you are related to that person through. Also the marriage of close cousins can make the predicted relationship appear closer than it is because the same genes are passed down multiple times.
Who Can Test
Males
Females
Why? Autosomal DNA is inherited from both parents. Therefore, an autosomal DNA test may be taken by either a male or a female

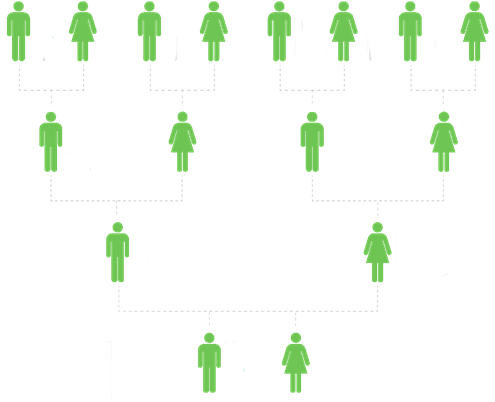
Just like the Image represents the atDNA looks at the DNA that you inherited from all your ancestors.
